New Options in an Evolving Market

Just a few years ago, choosing a vehicle often came down to one question: gas or diesel? Today, the landscape has expanded dramatically. With growing interest in sustainability, stricter emissions regulations and rising fuel costs, electric and hybrid vehicles now account for a significant share of new car sales.
Whether you're shopping for efficiency, performance or long-term value, it’s worth understanding the key differences between conventional gas engines, hybrids and electric vehicles. This guide breaks down the pros and cons of each to help you make a confident, informed decision.
Conventional Gas-Powered Vehicles
Gasoline-powered internal combustion engines remain a staple on today’s roads, powering millions of cars, trucks and SUVs. While the technology dates to the 19th century, modern engines have evolved significantly to deliver the performance, efficiency and reliability drivers expect.
How Gas Engines Work
The heart of a gasoline engine is the four-stroke combustion cycle, which converts fuel into motion through a series of precisely timed mechanical events:
- Stroke 1 – Intake: The piston moves downward, drawing in a mixture of air and fuel through the open intake valve.
- Stroke 2 – Compression: The intake valve closes and the piston moves back up to compress the air/fuel mixture.
- Stroke 3 – Combustion (Power): When the piston is at the top, the spark plug fires to ignite the air-fuel mixture. The combustion pushes the piston back down.
- Stroke 4 – Exhaust: The exhaust valve opens and the piston returns to the top, expelling exhaust out of the cylinder.
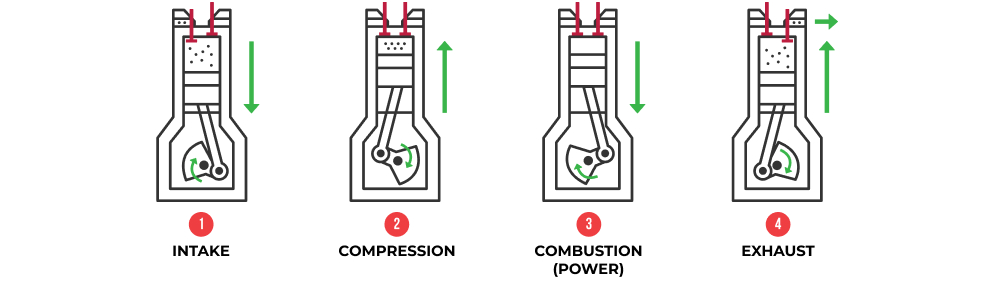
This cycle repeats rapidly – hundreds of times per minute in each cylinder—creating the power that moves your vehicle.
Pros of Gas Engines:
- Lower Upfront Cost – Typically more affordable than hybrid or electric vehicles.
- No Range Anxiety – Average range of 300-400 miles per tank.
- Strong Performance – Has more power for accelerating and towing/hauling.
- Convenient Refueling – Gas stations are widely available.
Cons of Gas Engines:
- Environmental Impact – Produces greenhouse gases that contribute to air pollution.
- Fossil Fuel Dependency – Powered by gasoline, a non-renewable resource.
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Concerns about fuel availability and the environmental impact of internal combustion engines have sparked a race among automakers to develop electric vehicles (EVs) that achieve widespread public adoption. Unlike gas-powered vehicles, EVs rely on battery power to drive an electric motor that turns the wheels.
At first glance, EVs often resemble their gas-powered counterparts. But under the hood, the difference is clear: fewer moving parts, no engine block and a streamlined powertrain built around electricity.
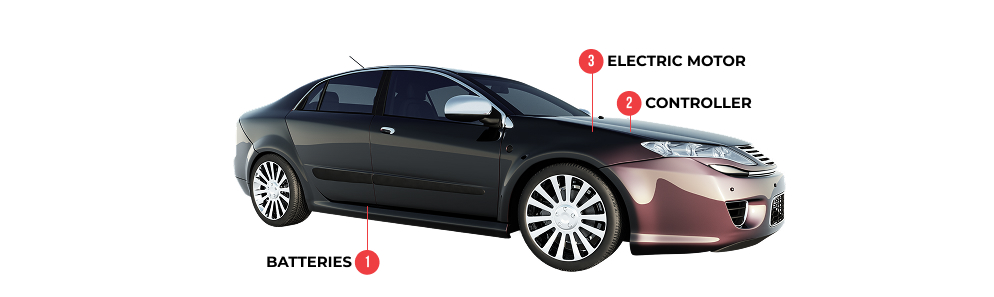
Key Components of an EV Engine:
- Battery Pack – Primary power source of vehicle; located beneath the vehicle floor or in the trunk.
- Controller – Converts battery power and regulates the flow of electricity to the motor.
- Electric Motor – Uses energy from the controller to propel the vehicle.
Power-Saving Technologies:
- Auto Start-Stop – Automatically shuts off the engine when the vehicle stops and restarts it when the accelerator is pressed, reducing idle energy use.
- Regenerative Braking – Captures energy during braking or coasting and feeds it back into the battery, improving efficiency and range.
Pros of EV Engines:
- Zero Emissions – No exhaust means reduced environmental impact.
- Fewer Moving Parts – Less wear and wear leads to reduced repairs.
- Minimal Routine Maintenance – No oil changes, spark plugs or transmission fluid.
- Home Charging Convenience – Install a home charger and start each day with a full charge.
Cons of EV Engines:
- Limited Driving Range – Many models offer 150-300 miles today, but older or entry-level EVs may fall short.
- Longer Charging Times – Full charges can take 4-8 hours at home; fast chargers aren’t always available.
- Difficulty Finding a Charger – Public stations are expanding but not as plentiful as gas stations.
- Higher Upfront Cost – EVs often come with a premium price tag.
- Battery Expense – Battery packs can cost $1,000-4,000 or more to replace, though the warranty often covers 8-10 years.
- Compact Design – Some EVs offer less seating or cargo space compared to traditional vehicles.
Hybrid Vehicles: Bridging Gas and Electric Power
Hybrid vehicles combine the gasoline engines and electric motors to boost fuel economy and reduce emissions. Effective in stop-and-go traffic, hybrids offer a more efficient alternative to traditional gas-powered cars.
Along with auto start-stop and regenerative braking – features shared with EVs – hybrids use electric power assist to support the engine during acceleration, hill climbs, and passing. This allows for smaller, more efficient engines without sacrificing performance.
There are several types of hybrid vehicles available today.
| Type | Description | Fuel Savings |
|---|---|---|
| Full Hybrid | Can drive short distances on electric power. | High |
| Mild Hybrid | Electric motor assists but never powers the vehicle independently. | Moderate |
| Micro-Hybrid | Limited electrification – typically limited to start-stop functionality. | Low |
| Plug-In Hybrid | Larger batteries allow charging via outlet; can run fully electric for short trips before switching to gasoline. | High |
Pros of Hybrid Engines:
- Improved Fuel Economy – Hybrids optimize fuel use by switching between electric and gas power.
- Fewer Fill-Ups – Reduced gas use means fewer trips to the pump and long-term savings.
- Lower Emissions – Less gas use means fewer emissions than gas-only vehicles.
- Higher Resale Value – Proven reliability and fuel savings help hybrids hold their value.
Cons of Hybrid Engines:
- Higher Purchase Price – Battery system and advanced drivetrains add to upfront cost.
- Costly Repairs – Dual powertrains mean more parts and potentially higher service bills.
- Reduced Acceleration and Torque – Typically hybrids prioritize efficiency over power.
Learn more about the brands of DRiV, find your car part or find where to buy your auto part today.
The content in this article is for informational purposes only. You should consult with a certified technician or mechanic if you have questions relating to any of the topics covered herein. DRiV and its affiliates (including Federal-Mogul Motorparts LLC) will not be liable for any loss or damage caused by your reliance on any content.


